-
Article
-
Development of Tidal-Induced Local Scour Around Offshore Structure: A Case Study in Shinan Area
조석에 의한 해상 구조물 주변 국지세굴 발달 양상: 신안해역 사례
-
JI HEE OH, BYEONG JIN JEON, SEONG WOON JEONG, JAE HYEOK SHIN, INSUNG JEON AND HO KYUNG HA
오지희, 전병진, 정성운, 신재혁, 전인성, 하호경
- Local scour is a geomorphological process around offshore structures and directly affects their structural stability. In tidal-dominated regions, in particular, the tidal …
국지세굴은 해상 구조물 주변에서 발생하는 해저 지형 변화로, 구조물의 안정성에 직접적인 영향을 미치는 중요한 현상이다. 특히, 조석 흐름이 지배적인 해역에서는 조류의 비대칭성으로 …
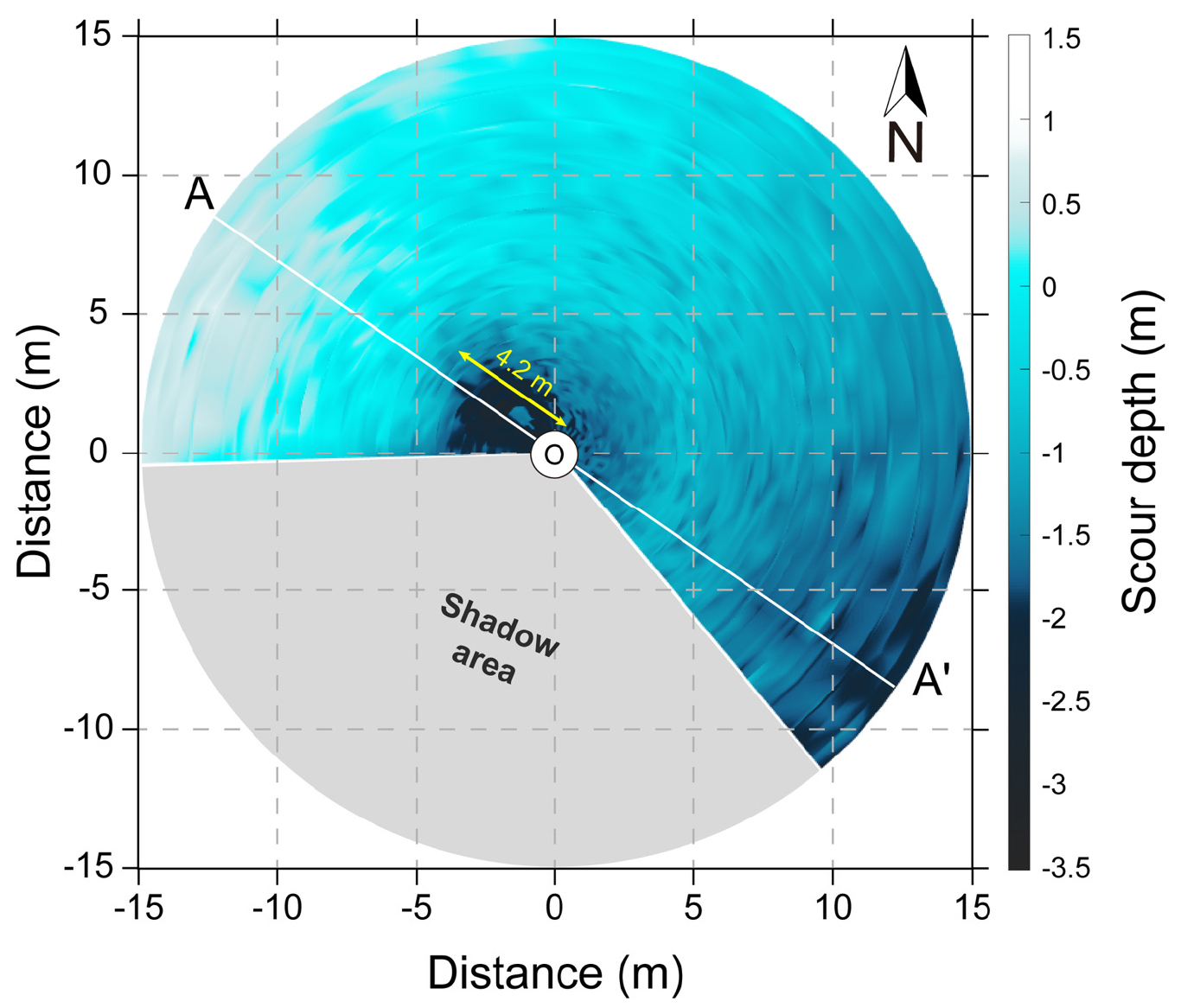
- Local scour is a geomorphological process around offshore structures and directly affects their structural stability. In tidal-dominated regions, in particular, the tidal asymmetry can induce directional bias in the development of local scour. In order to investigate the development characteristics of local scour under tidal forcings, a rotary sonar profiler was installed on a jacket-type offshore platform located within the Shinan Offshore Wind Farm, Jeollanam-do for 22 days from April 18 to May 9, 2024. The in-situ mooring observations revealed the formation of an asymmetric local scour with deeper scour depth in the ebb direction because of an ebb-dominant tidal asymmetry. On average, the scour depth in the ebb direction (1.83 m) was approximately 31.6% deeper than that in the flood direction (1.39 m). The maximum scour depth reached 3.11 and 3.03 m during the spring and neap tides, respectively. Although the maximum scour depth varied during the mooring period, it remained consistently around 2.85 m, indicating the local scour had generally reached a stabilization state, despite short-term fluctuations by tidal variations. The scour slopes in the ebb (<26°) and flood (<16°), referenced to the local seabed, were both lower than the typical angle of repose (~32°) commonly observed in tide-dominant environments. It is speculated that the repetitive cycles of erosion and redeposition contributed to the development of a relatively gentle and stable scour slope. Sediments eroded during the scour process were transported by tidal currents, and subsequently redeposited as a 0.5 m-high mound on the northwestern side of the structure. This study quantitatively elucidated the influence of tidal asymmetry on the local scour morphology and the structural stability around an offshore platform. Furthermore, the results could serve as baseline data for predicting and managing benthic morphological changes around offshore platforms.
- COLLAPSE
국지세굴은 해상 구조물 주변에서 발생하는 해저 지형 변화로, 구조물의 안정성에 직접적인 영향을 미치는 중요한 현상이다. 특히, 조석 흐름이 지배적인 해역에서는 조류의 비대칭성으로 인해 세굴의 깊이와 형태가 특정 방향으로 발달하는 경향이 있다. 본 연구에서는 조석 주기에 따른 국지세굴의 발달 양상을 파악하기 위해, 전라남도 신안 해상풍력단지 내 자켓형 해상 플랫폼에 회전식 소나 프로파일러(rotary sonar profiler)를 설치하고, 2024년 4월 18일부터 5월 9일까지 총 22일간 현장 관측을 수행하였다. 관측 결과, 조석 방향을 따라 비대칭적인 국지세굴이 관측되었으며, 연구지역의 낙조 우세 비대칭형 조석으로 인해 낙조 방향에서 더 깊은 세굴 깊이가 확인되었다. 평균 세굴 깊이는 창조(1.39 m)보다 낙조(1.83 m) 방향에서 약 31.6% 더 깊었다. 최대 세굴 깊이는 대조기와 소조기에서 각각 3.11과 3.03 m까지 도달하였다. 최대 세굴 깊이는 지속적으로 증감하였으나, 평균적으로 2.85 m에서 안정적으로 유지되었다. 이는 국지세굴이 초기 및 발달 단계를 지나 점차 안정화되었으며, 조석에 기인한 단기적 변동이 존재함에도 불구하고 전체적으로는 안정화 상태에 도달했음을 시사한다. 세굴 경사는 바닥면을 기준으로 낙조(<26°)와 창조(<16°) 방향 모두에서 왕복성 조류가 지배적인 환경에서 일반적으로 관측되는 안식각(~32°)보다 작았으며, 이는 반복되는 퇴적물 침식과 재퇴적 과정으로 인해 경사면이 완만하게 유지된 것으로 해석된다. 세굴 과정에서 침식된 퇴적물은 구조물 주변의 조석에 의해 북서 방향 외곽에 약 0.5 m 높이로 재퇴적되었다. 본 연구는 조석의 비대칭성이 해상 플랫폼 주변의 국지세굴 형태와 구조물의 안정성에 미치는 영향을 정량적으로 규명하였다. 현장 관측 결과는 향후 해상 플랫폼 주변 해저 지형 변화를 예측하고 관리하는 데 유용한 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Development of Tidal-Induced Local Scour Around Offshore Structure: A Case Study in Shinan Area
-
Article
-
Analysis of the Morphological and Phylogenetic of Tetramphora Sulcata in Korea Tidal Flat
국내 저서 환경에서 출현한 Tetramphora sulcata의 형태 및 계통 발생학적 특성 분석
-
JEONGYUNG JIN, BYOUNGSEOK KIM, SOYEON KIM, BYEOL KIM, CHUNG HYEON CHOI, SUK MIN YUN AND JONG-GYU PARK
진정융, 김병석, 김소연, 김별, 최충현, 윤석민, 박종규
- To study diatoms within the coastal benthic environment of Korea, surface sediments were collected in Pohang in May 2021, resulting in the …
한국 연안 저서환경의 규조류 연구를 위해 2021년 5월 포항에서 표층 퇴적물을 채집하여 국내 미기록 Tetramphora 1종을 발굴하였다. 주사전자현미경(SEM)과 광학현미경으로 형태를 관찰하였고, rbc …
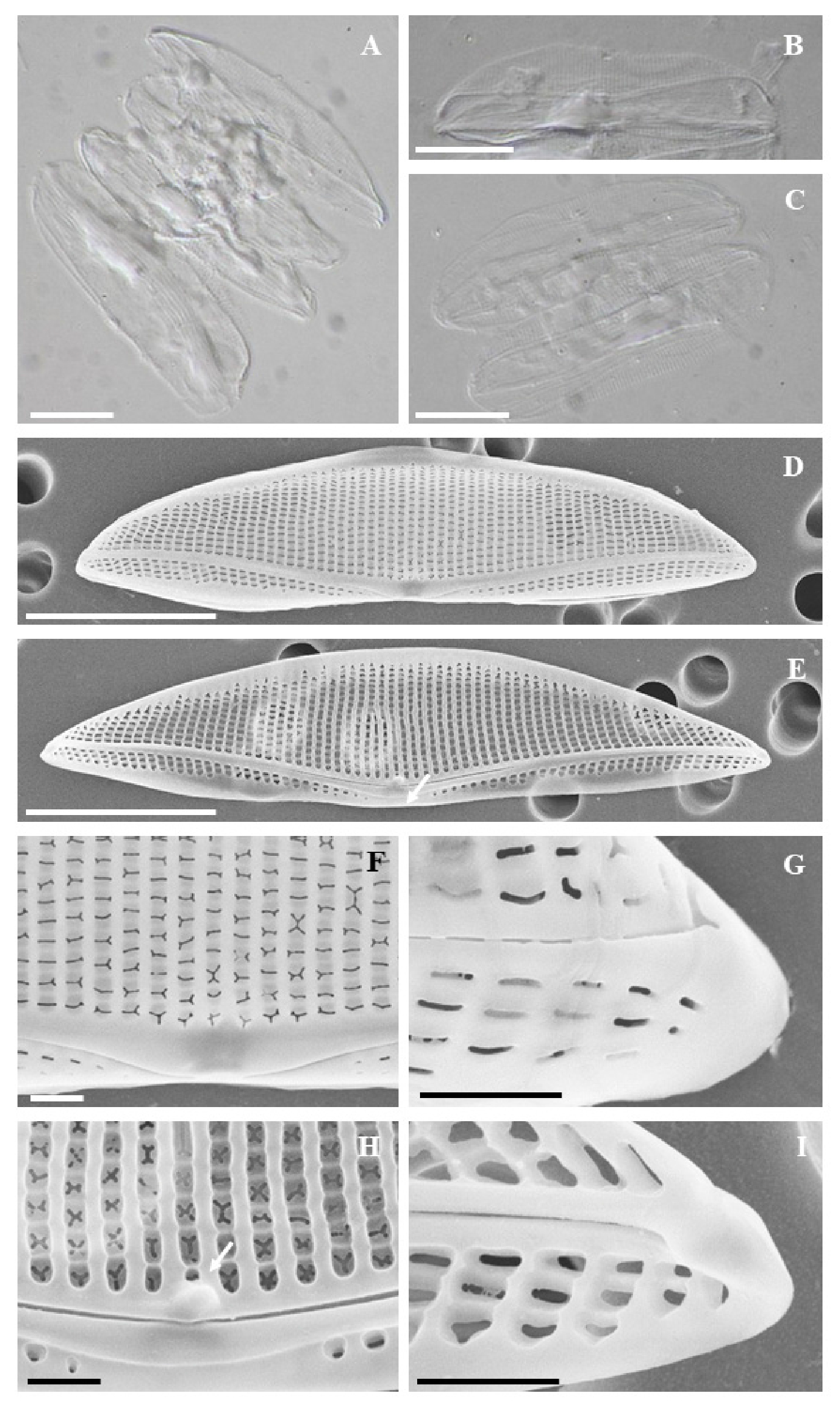
- To study diatoms within the coastal benthic environment of Korea, surface sediments were collected in Pohang in May 2021, resulting in the discovery of a species of Tetramphora that had not been previously documented in Korea. The morphological characteristics were observed using both scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and optical microscopy, while its phylogenetic position was confirmed through the gene analysis of rbcL gene. The species under study exhibits the typical characteristics of Tetramphora, including less biarcuate raphe and siliceous clusters in the central region of the valve. The diatom measures is 35–39 μm in length and 8–9 μm in width, displaying 19 striae per 10 μm on the dorsal valve and 20 striae per 10 μm on the ventral valve. SEM observations revealed that a fascia is present in the center of the ventral valve, with a protrusion at the inner distal end of the raphe. The morphological characteristics of the species studied correspond with those of T. sulcata, and genetic analysis further supports its phylogenetic relationship with this species. This study represents the first report of T. sulcata in the coastal waters of Korea.
- COLLAPSE
한국 연안 저서환경의 규조류 연구를 위해 2021년 5월 포항에서 표층 퇴적물을 채집하여 국내 미기록 Tetramphora 1종을 발굴하였다. 주사전자현미경(SEM)과 광학현미경으로 형태를 관찰하였고, rbcL 유전자 분석을 통해 분자계통분류학적 위치를 확인하였다. 연구 종은 중앙부에서 양 정축 끝으로 발달하는 완만한 호형의 raphe와 중앙부에 규산질이 뭉쳐져 있는 전형적인 Tetramphora의 특징을 하고 있으며, 길이 35-39 μm, 폭 8-9 μm, 10 μm 당 stria 개수는 등과 배에서 각각 19개, 20개이다. SEM에서 관찰한 세부 형태로 배 쪽 세포 중앙부에 fascia가 존재하고 내부 distal raphe end에 돌출부를 가진다. 연구 종은 보고된 T. sulcata와 형태 특징이 같고, 유전자 분석을 통한 계통분류학적 위치가 일치하였다. 본 연구를 통해 T. sulcata가 국내 해역에 분포하고 있음을 최초로 보고한다.
-
Analysis of the Morphological and Phylogenetic of Tetramphora Sulcata in Korea Tidal Flat
-
Article
-
Meiofaunal Biofouling on the Marine Plastic Debris Washed Ashore in Polluted-Hot-Spots of Korea in Summer
하계 해안 쓰레기 밀집 해역 출현 플라스틱 서식 중형저서부착생물 특성
-
HA KYONG CHOI, MINJU KIM, HYEON KIM AND JUNG-HOON KANG
최하경, 김민주, 김현, 강정훈
- We investigated the meiofaunal biofouling (40-1,000 ㎛) on marine plastic debris (MPD) collected in highly polluted waters during the summer of 2021 …
2021년 하계(8-9월)에 해안 쓰레기 밀집 해역에서 채집한 해양 플라스틱 쓰레기에 서식하는 중형저서부착생물(40-1,000 ㎛)의 부착 특성과 채집지역 간 차이를 조사하였다. 총 6종류의 플라스틱 …
- We investigated the meiofaunal biofouling (40-1,000 ㎛) on marine plastic debris (MPD) collected in highly polluted waters during the summer of 2021 (August-September), in order to analyze the MPD related organisms with the collection site specific environment. A total of six shapes of plastic debris (ropes, styrofoam buoys, plastic bottles, plastic containers, plastic bags, and sponges) were collected, categorized into six polymer types (PP, PS, PET, LDPE, HDPE, EPS), and 10 biota were represented. The relationship between the surface area of all plastic litter and the abundance of organisms was not statistically significant (r2=0.02, n=24, p=0.48). However, the highest abundance was observed in PP litter with the smallest surface area (sieve size 40-60 ㎛: 68 inds./0.1 m2, 60-300 ㎛: 376 inds./0.1 m2, 300-1,000 ㎛: 489 inds./0.1 m2). The smallest size group (sieve size 40-60 ㎛) showed a significant difference in abundance by polymer types (F=6.693, p < 0.01), while the other size groups (sieve size 60-300 ㎛ and 300-1,000 ㎛) did not differ (p > 0.05). The main dominant taxa were nematodes in the size group (sieve size 40-60 ㎛) (77.8% on average), while the other size groups (sieve size 60-300 ㎛ and 300-1,000 ㎛) were dominated by bryozoans, foraminiferans, bivalves and gastropods. The mean abundance of all size groups was higher in Myeongji (249 inds./0.1 m2) and Heungnam Beach (482 inds./0.1 m2), which had the lowest salinity (0.2 psu), compared to the other collection sites (65 inds./0.1 m2), but there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the sampling sites. In summary, the abundance of summer meiofaunal biofouling was significantly associated with a specific polymer (PP) rather than litter area, and the size group dominated by nematodes (sieve size 40-60 ㎛) showed polymer-specific differences of abundance, indicating that PP litter may be a favorable habitat for nematodes.
- COLLAPSE
2021년 하계(8-9월)에 해안 쓰레기 밀집 해역에서 채집한 해양 플라스틱 쓰레기에 서식하는 중형저서부착생물(40-1,000 ㎛)의 부착 특성과 채집지역 간 차이를 조사하였다. 총 6종류의 플라스틱 쓰레기(밧줄, 스티로폼 부이, 페트병, 플라스틱 용기, 플라스틱 봉지, 스폰지)가 채집되어 6가지 재질(PP, PS, PET, LDPE, HDPE, EPS)로 구분되었고, 10개 생물분류군이 출현하였다. 모든 플라스틱 쓰레기의 표면적과 출현한 생물 개체수 간의 관계는 통계적으로 유의하지 않았다(r2=0.02, n=24, p=0.48). 반면, 표면적이 가장 작은 PP재질의 쓰레기에서 가장 높은 개체수가 관찰되었다(체 크기 40-60 ㎛: 68 inds./0.1 ㎡, 60-300 ㎛: 376 inds./0.1 ㎡, 300-1,000 ㎛: 489 inds./0.1 ㎡). 가장 작은 크기그룹(체 크기 40-60 ㎛)의 개체수가 재질별 유의한 차이를 나타낸 반면(F=6.693, p < 0.01), 다른 크기그룹(체 크기 60-300 ㎛ 와 300-1,000 ㎛)의 개체수는 재질별 차이가 없었다(p > 0.05). 주요 우점분류군은 선충류가 가장 작은 크기그룹(체 크기 40-60 ㎛)에서 가장 우점했고(평균 77.8%), 다른 크기그룹(체 크기 60-300 ㎛, 300-1,000 ㎛)에서는 태형동물, 유공충류, 이매패류와 복족류가 우점하였다. 모든 크기그룹에서 출현한 평균 개체수는 염분이 가장 낮은(0.2 psu) 명지(249 inds./0.1 ㎡)와 흥남해수욕장(482 inds./0.1 ㎡)에서 다른 해역(65 inds./0.1 ㎡)에 비해 높았으나, 채집 해역간 유의한 차이는 없었다(p > 0.05). 요약하면, 하계 중형저서부착생물의 출현개체수가 쓰레기의 면적보다 특정 재질(PP)과 관련이 있고, 선충류가 우점한 크기그룹(체 크기 40-60 ㎛)이 재질별 차이를 나타낸 것으로 보아, PP재질의 쓰레기가 선충류의 유리한 서식환경일 수 있음을 시사한다.
-
Meiofaunal Biofouling on the Marine Plastic Debris Washed Ashore in Polluted-Hot-Spots of Korea in Summer
-
Review
-
Phosphorus Fractionation and Biogenic Phosphorus in Sediments Affected by Aquaculture Activities: Importance as a Proxy for Assessing Environmental Effects of Fish Farming
양식장 퇴적물 내 인 형태별 분획 및 생물기원 인의 분포 특성: 어장환경평가 지표로서의 중요성
-
JIN-SOOK MOK, JUNG-HO HYUN, SANG BEOM BAEK, AYEON CHOI AND HANEUL KIM
목진숙, 현정호, 백상범, 최아연, 김하늘
- The expansion of aquaculture has led to phosphorus (P) accumulation in coastal sediments through the deposition of uneaten fish feed and feces. …
양식 산업의 확장은 잉여 사료와 배설물 침강을 통해 연안 퇴적물 내 인 축적을 초래하였다. 본 논문은 어류와 패류 양식장 퇴적물 및 사료(배합사료와 …
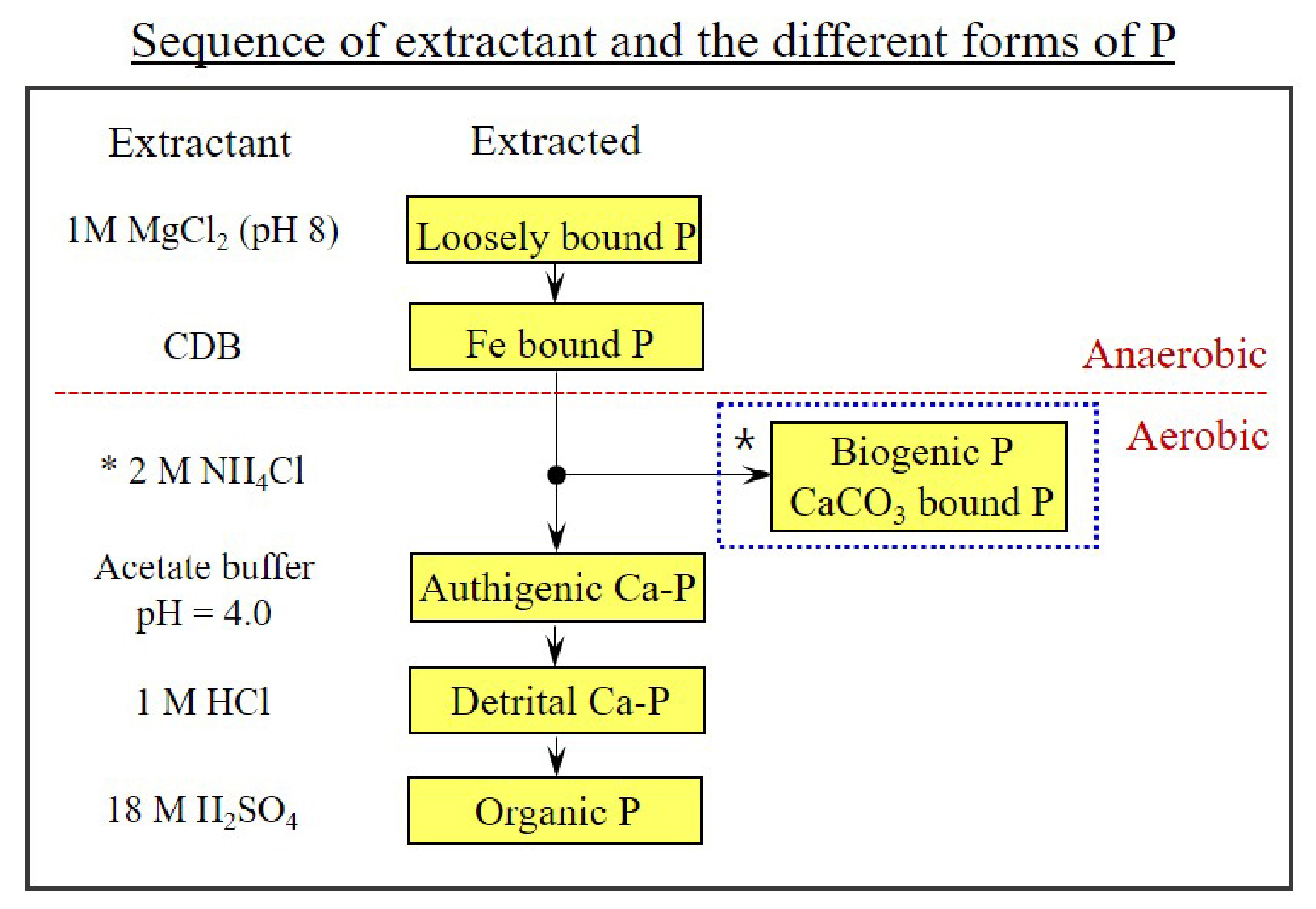
- The expansion of aquaculture has led to phosphorus (P) accumulation in coastal sediments through the deposition of uneaten fish feed and feces. This study compared the distribution of phosphorus forms in finfish and shellfish farm sediments and two types of fish feed, extruded pellet (EP) and raw feed (RF), to analyze changes in P fractions in coastal sediments caused by aquaculture activities and highlights the significance of biogenic phosphorus (Bio-P) as a relevant proxy for evaluating farming effects on surface sediments. Sequential extraction analysis showed that total phosphorus (TP) contents in the finfish farm sediments (up to 256 μmol g-¹) were approximately 80 times higher than those in the shellfish farm sediments (up to 3.76 μmol g-¹), indicating significantly greater P discharge from the finfish farms. In addition, P contents in the control site near the finfish farms (up to 40.2 μmol g-¹) were 12.6 times higher compared to shellfish farms, underscoring the dominant impact of finfish farming on P accumulation in surrounding sediments. The P speciation showed that authigenic calcium-bound P (Aut-P, 38~40% of total P) precipitation could be promoted from the regeneration of inorganic P through organic matter mineralization (e.g., sulfate reduction process) in the organic-rich finfish and shellfish farm sediments. Biogenic phosphorus (Bio-P, 77.9 μmol g-¹, 30.5% of total P) in the finfish farm sediments was 25 times higher compared to the control sediments (3.06 μmol g-¹, 7.6% of total P), suggesting that the deposition of uneaten feed and feces is directly responsible for the accumulation of Bio-P in the surface sediments of the farms, which can be used as an index to evaluate environmental conditions in sediments. The analysis of P speciation in EP and RF showed a high portion of Bio-P (32.1~34.8% of total P), similar to finfish farm sediments. In the RF, the loosely sorbed P (Lsor-P) accounted for 52.8% of the total P, which means the possibility of accumulating bioavailable P that contributes to the enhancement of benthic P release, and ultimately suggests that it may have a relatively greater impact on P pollution in coastal environments compared to the EP (Lsor-P; 32.1% of total P). P speciation analysis and Bio-P quantification in aquaculture sediments are critical for evaluating pollution sources, predicting eutrophication risks, and establishing operational guidelines. Understanding P dynamics coupled to iron-sulfur cycles can pave the way for sustainable fishery management.
- COLLAPSE
양식 산업의 확장은 잉여 사료와 배설물 침강을 통해 연안 퇴적물 내 인 축적을 초래하였다. 본 논문은 어류와 패류 양식장 퇴적물 및 사료(배합사료와 생사료)에서 분석된 인(P)의 형태별 분포 자료를 비교 분석하여 양식 활동에 따른 연안 퇴적물 내 인의 형태별 분포 변화 및 어류 양식장 퇴적물 내 생물기원 인 연구의 필요성에 대해 고찰하였다. 연속추출법(sequential extraction method)을 통해 분석한 결과, 총인의 함량이 수하식 패류 양식장 퇴적물(최대 3.76 μmol g-1)에 비해 가두리 어류 양식장 퇴적물(최대 256 μmol g-1)에서 약 80배 높은 것으로 나타나, 어류 양식장으로부터의 인 배출 영향이 매우 크다는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 또한 어류 양식장의 대조구(최대 40.2 μmol g-1)에서도 패류 양식장보다 약 12.6배 높게 나타남에 따라 어류 양식 활동이 주변 퇴적물 내 인 축적에 상당한 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 인의 형태별 분석 결과는 유기물이 풍부한 어류와 패류 양식장 퇴적물에서 유기물 분해(예, 황산염 환원 과정)를 통한 무기 인의 재생으로부터 자생성 칼슘 결합인(Aut-P) 침전이 촉진(총인의 38~40%)될 수 있음을 보여주었다. 생물기원 인(Bio-P)은 어류 양식장 퇴적물(77.9 μmol g-1)에서 대조구 퇴적물(3.06 μmol g-1)에 비해 25배 더 높게 나타났으며, 총인에서 Bio-P가 차지하는 비율도 30.5%로 대조구 퇴적물(7.6%)보다 4배 정도 높은 것으로 나타났다. 이러한 결과들은 잉여사료와 배설물의 침강이 양식장 표층 퇴적물(0-1 cm) 내 Bio-P의 축적에 직접적인 책임이 있음을 시사하며, Bio-P가 양식장이 운영되는 퇴적물 내 환경 조건을 평가하는 지표로 활용될 수 있음을 나타낸다. 한편, 배합사료와 생사료 내 인의 형태별 분석 결과, 어류 양식장 퇴적물과 유사하게 높은 Bio-P 비율(총인의 32.1~34.8%)을 나타냈다. 생사료의 경우, 약하게 흡착된 인(Lsor-P)의 비율이 총인의 52.8%였으며, 이는 저층 인 용출 향상에 기여하는 생물이용이 가능한 인의 축적 가능성을 의미하며, 궁극적으로 생사료가 배합사료(Lsor-P; 총인의 32.1%)와 비교해 연안 환경 내 인 오염에 상대적으로 더 큰 영향을 줄 수 있음을 시사한다. 양식장 퇴적물 내 형태별 인 분석 및 생물기원 인 정량화는 양식장의 오염원에 대한 평가, 부영양화 위험성 예측, 양식장 운영 지침 마련에 필수 분야로 여겨지며, 철-황 순환과 연계된 인 거동 이해를 통해 지속 가능한 어업 관리를 위한 토대를 마련할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Phosphorus Fractionation and Biogenic Phosphorus in Sediments Affected by Aquaculture Activities: Importance as a Proxy for Assessing Environmental Effects of Fish Farming
-
Review
-
Marine Geological Survey in the Arctic Ocean Using the Icebreaker ARAON
쇄빙선 아라온호를 이용한 북극해 해저지질조사
-
JONG KUK HONG AND YOUNG KEUN JIN
홍종국, 진영근
- During the glacial period, the Arctic Ocean was a much smaller, enclosed basin disconnected from the Pacific Ocean. Following the last glaciation, …
빙하기 동안 북극해는 현재보다 면적이 훨씬 작고 태평양과의 연결이 차단된 폐쇄적 해역이었다. 그러나 빙하기 이후 급격한 해수면 상승으로 인해 해역 면적이 두 …
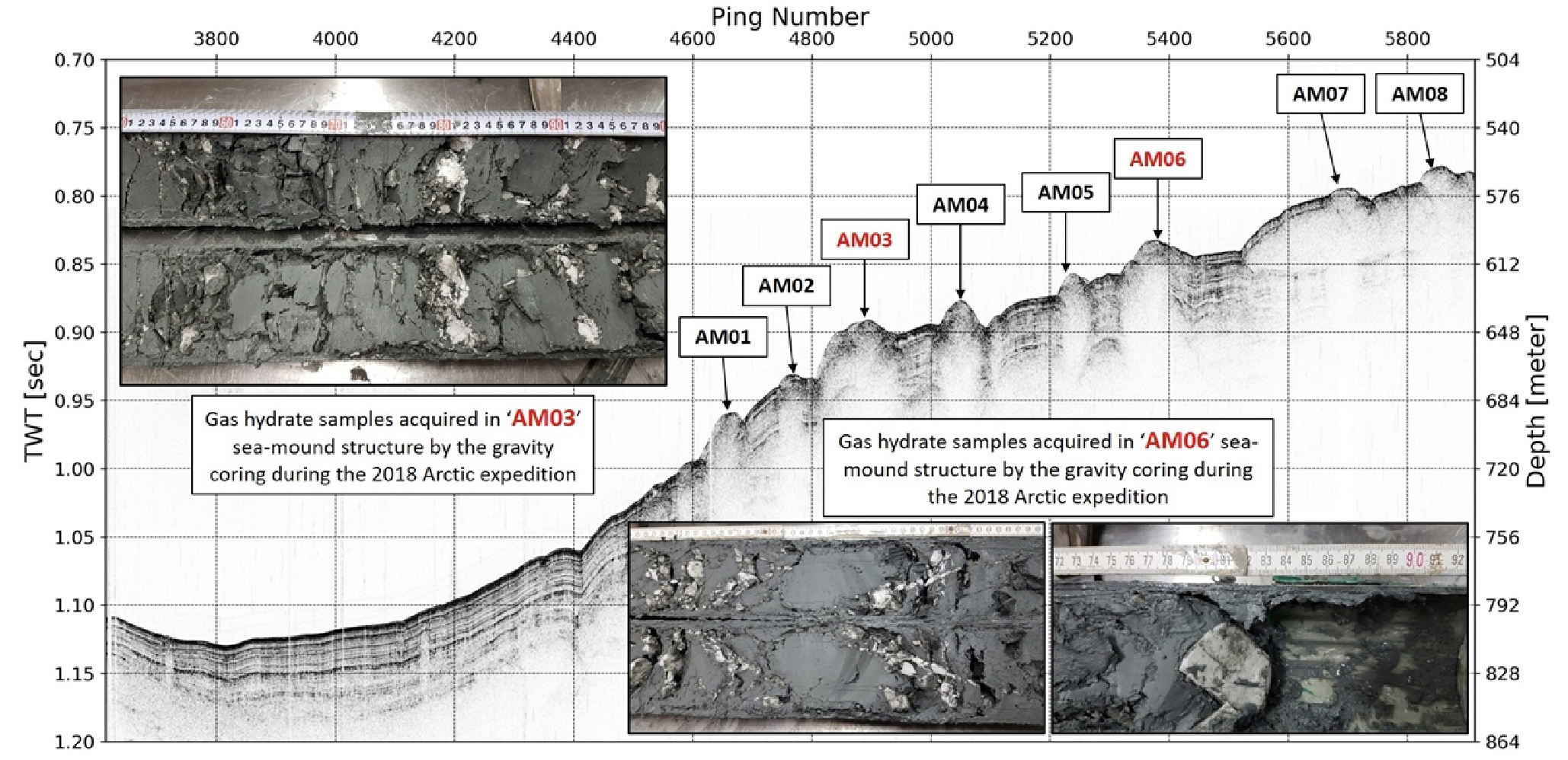
- During the glacial period, the Arctic Ocean was a much smaller, enclosed basin disconnected from the Pacific Ocean. Following the last glaciation, a rapid rise in sea level led to extensive marine transgression, doubling the ocean’s size and significantly altering its seafloor environment. Submarine permafrost, gas hydrates, and methane seepage, primarily distributed along the continental shelf, have undergone gradual changes due to sea-level fluctuations and global warming, contributing to the instability of the seafloor. To systematically investigate these environmental changes, Korea deployed its first icebreaking research vessel, IBRV Araon, built in 2009, into the Arctic Ocean. This review paper presents key findings from seafloor geological investigations conducted in the Arctic Ocean since 2012. Major results include: (1) the formation of various glacial features and depositional records on the continental shelf due to repeated advances and retreats of marine-based ice sheets during the Pleistocene; (2) the first discovery of gas hydrates and widespread bottom-simulating reflectors (BSRs) in the southwestern Chukchi Sea; and (3) the identification of mud volcanoes and extensive submarine permafrost degradation in the Canadian Beaufort Sea, accompanied by seafloor features such as thermokarst, craters, and pingo-like structures. These findings enhance our understanding of the interactions among glaciation, climate change, and seafloor geology, and provide a foundation for future drilling and long-term monitoring aimed at responding to environmental changes in the Arctic region.
- COLLAPSE
빙하기 동안 북극해는 현재보다 면적이 훨씬 작고 태평양과의 연결이 차단된 폐쇄적 해역이었다. 그러나 빙하기 이후 급격한 해수면 상승으로 인해 해역 면적이 두 배 이상 확장되었고, 해저 환경에도 중대한 변화가 나타났다. 특히, 해수면 변화와 지구온난화에 따라 북극해 대륙붕을 중심으로 해저 영구동토층이 붕괴되고 가스하이드레이트가 해리되면서 다량의 메탄이 분출하는 등 해저 환경의 불안정성이 가속화되고 있다. 우리나라는 이러한 북극해 해저지질환경 변화에 대한 체계적인 연구를 위하여 2009년에 건조된 국내 최초의 쇄빙연구선 아라온호를 투입하였다. 본 논문은 아라온호를 이용하여 2012년부터 북극해에서 수행한 해저지질 조사 결과를 소개하고자 한다. 대표적인 성과로는 (1) 플라이스토세 동안 반복된 빙상의 확장과 후퇴로 인해 형성된 다양한 빙하성 지형과 퇴적 기록, (2) 척치해 남서부에서의 가스하이드레이트 최초 발견과 광범위한 해저면 모방 반사면(BSR, bottom simulating reflector)의 확인, (3) 캐나다 보퍼트해에서의 진흙화산 및 해저 영구동토층 융해로 인한 다양한 지형 변화 발견 등이 있다. 이러한 연구결과는 빙하, 기후, 해저지질 간 상호작용에 대한 이해를 증진시키며, 북극 지역의 기후 변화에 따른 해저 지질환경 변화 예측과 대응 전략 수립을 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 것이다.
-
Marine Geological Survey in the Arctic Ocean Using the Icebreaker ARAON
-
Newsletter

-
The Korean Society of Oceanography Newsletter
한국해양학회 소식지
-
2025.5
2025. 2호
-
The Korean Society of Oceanography Newsletter
Journal Informaiton
 The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography
The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography
The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography











